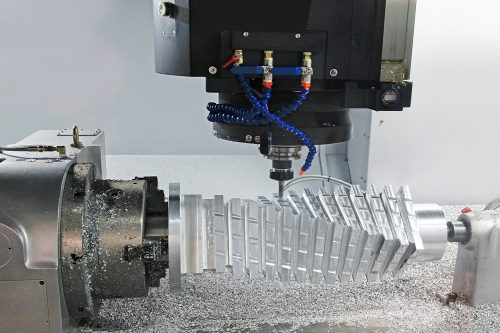
Sheet metal fabrication is instrumental to many industries that power the world. Discover the different world of sheet metal fabrication, where skilled craftspeople produce vital components from cars and planes to medical equipment and infrastructure. Also, from precision cutting to complex design, sheet metal fabrication is the foundation of almost every product we rely on.
When it comes to sheet metal fabrication, not all processes and methods are created equal to craft complex shapes through high volume operations.
Depending on the industry, manufacturers will likely require customized metal components to serve as suitable materials for their manufacturing needs. This may include creating holes with varying hole diameters, cutting multiple straight edges, or adding specialized surface finishes at the end of the process.
In addition, industries tend to work with sheet metal of varying thicknesses, which can add another layer of complexity to sheet metal fabrication processes. The material thickness often determines the best tools for sheet metal fabrication. It is also used for other factors, such as the metal component’s geometry and the sheet metal design.
So, before you can launch sheet metal fabrication processes in high volumes, it’s important to understand the fundamentals of metal fabrication. From the initial engineering drawings to the sheet metal design to testing the final sheet metal parts, there are several steps to crafting the products that drive manufacturing industries around the globe.
Table of Contents
The Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
Prototype Development and Testing
Design Tips for Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tools
Common Sheet Metal Processes
Additional Types of Cutting Methods
Steelway Laser Cutting Can Help with Sheet Metal Fabrication
What is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Sheet metal fabrication is a process that allows companies to manufacture different products or metal components using a combination of compatible materials and techniques. Using flat metal sheets, these metal parts are created to precise specifications. They result in metal components that perfectly integrate into a broader project or serve as a stand-alone product.
Different types of machinery are used to form, bend, cut, and combine metal sheets into preferred shapes. Therefore, the sheet metal fabrication process can be used with various metals, such as stainless steel, mild steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and more. In addition, sheet metal finishes may be applied at the end of the fabrication process to add extra features to the finished metal parts. For instance, they use a chromate conversion coating, powder coating, or a wear-resistant layer for extra corrosion resistance.
The Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
Sheet metal fabrication processes can vary based on a range of factors. Such as sheet thickness, sheet stock, and production volumes – as well as the exact design of the metal parts that need to be created. Regardless (and generally speaking), the fabrication process involves the following steps.
Sheet metal parts design
The sheet metal fabrication process begins with an idea that translates to a design. Depending on the intricacy of the metal part involved, design engineers may craft 3D models that include the requirements for wall thickness, hole orientation, bend allowance, and other features. A flat pattern may only be needed to move forward if the designed metal components are simple (like creating straight edges on thin metal sheets).
Prototype Development and Testing
Once the metal parts have been perfectly designed, engineers will typically utilize several processes to create prototypes of production parts. Material selection is an important first step to ensure that sheet metal fabricators can handle the sheet material. Then, the metal parts will be built on a small scale through varying methods like cutting, bending, or welding.
Surface finishes, like powder coating or powdered paint, can also improve the aesthetics of metal parts prototypes. Therefore, testing can begin after creating a small batch of metal parts.
Testing is arguably the most important step in the sheet metal fabrication process. Furthermore, it ensures the sheet metal parts can do the job and perform the function required in the manufacturing process.
Testing may involve visual inspection, such as checking for rough edges or a uniform thickness. However, it’s more productive to ensure that the metal parts can withstand real-world conditions. As a result, these small batches of sheet metal parts may be implemented on a small scale. It can ensure the physical properties of the parts won’t succumb to extreme heat, extreme cold, or other potentially detrimental conditions.
Once the sheet metal materials have been thoroughly tested, production volumes can increase with larger amounts of sheet stock, resulting in metal fabrication work on a grand scale.
Design Tips for Sheet Metal Fabrication
There are a few design tips to bear in mind for a smoother metal fabrication process which include the following.
- Be sure to specify the hole sizes, alignment, and locations in the designs of the metal parts. Hole diameters less than the material thickness may result in long burnish, high punch loading, and excessive burr. As a result, hole diameters should always be greater than the material thickness whenever possible.
- Also, the distance between holes should be at least twice the material thickness. Placement of the holes is essential as well for production. In metal parts that require a hole near the edge of the sheet material, the spacing between the hole and the edge of the metal sheet should be at least the length of the material thickness.
- Collars and bend relief near piercing areas can also help strengthen metal parts and components. Grain structures are also essential to avoid cracks in parts with tabs or lugs. (Lugs should also be perpendicular or a little less than 45 degrees toward the grain direction instead of parallel.)
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tools
Several tools and methods that can be used in sheet metal bending, cutting, forming, and assembly as sheet metals transform into specified shapes.
The most common tools are computer numerical control or CNC machines. These machines utilize computer files or CAD designs in the metal fabrication process. The CNC machine sends a machine code to the laser cutter to form the sheet metal parts to exact specifications.
Laser cutters have been involved in fabrication processes for decades. They are the preferred cutting mechanism for sheet metals and compatible materials, as their precision and lack of human error are unmatched.
When it comes to straightforward cutting processes, band saws, chop saws, miters, and cutting torches are also options for sheet metal fabrication. Though not as precise as laser cutting, these processes can tackle hard materials that require minimal and uncomplicated cuts.
Common Sheet Metal Fabrication Processes
Complicated and three-dimensional metal parts may require different fabrication processes in order to form a completed, desired shape. The most common forms of sheet metal fabrication processes are listed below.
Cutting
Cutting is usually the first step in the manufacturing process, and it uses specialized tools like laser cutters to craft the desired dimensions. When it comes to cutting, sheet metal fabrication can be considered a subtractive manufacturing process. This is because the metal parts are created by removing excess material from larger sheet metal.
Shear Cutting
In shear cutting, shear forces can cut through the sheet metal. Additionally, there are generally three options for this style of metal cutting: shearing, punching, and blanking. Shearing is generally suitable for metal sheets that don’t need clean finishes, like mild steel, brass, or aluminum. The punching process involves using this shear force to cut holes in the metal sheets. In addition, blanking is an economical method that entails removing a portion of sheet metal from a larger piece of stock metal.
Shearing forces can accommodate a wide range of simple projects in sheet metal manufacturing. However, sheet metal fabricators may want to cut sheet metals in more precise designs. This is where more modern methods like laser cutting come into play.
Laser Cutting
Simply put, laser cutting is the preferred method for achieving high-quality cuts at high volumes. An experienced laser cutting services provider can handle the most complicated projects using a high-powered laser beam to efficiently cut through the sheet stock. Utilized in top-quality sheet metal fabrication work, laser cutting ensures every metal part is cut to exact specifications. In addition, a laser cutting machine can eliminate scrap material or excess waste, or time delays due to human error.
Additional Types of Cutting Methods
Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting is a thermal process involving metal with ionized gas, known as plasma. This cutting method uses substantial heat to cut the sheet metal. This creates burrs and an oxidized zone close to the cut area. However, fast and precise plasma cutting works best on electrically conductive sheet metals. As a result, it’s a suitable method for cutting conductive materials with a medium thickness.
Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water to cut through sheet metal. It can be utilized for both soft and hard materials. Though waterjet cutting is one of several cutting processes available in sheet metal manufacturing, many modern companies still prefer laser cutting in the fabrication process due to its adaptability, low cost, and high production.
Remember that the type of cutting you choose may depend on your material selection. The thickness of your metal sheets and sheet metal materials, and the intricacy of the design, will determine the best path forward.
Bending
Bending is a process that creates a wide array of shapes and angles by adding simple bends to a piece of sheet metal. This sheet metal fabrication process uses a press brake machine to bend the metals into desired angles, forming the complete metal part.
Welding
Processes such as joining or assembly may also require welding methods for the sheet metal parts to be formed, assembled, and tacked into a specified position.
Welding is the process of joining sheet metal parts to form a single, larger metal part by heating the individual sheet metal pieces to their melting point.
There are different techniques involved in welding – including shielded metal arc welding, metal intel gas welding, and tungsten inert gas welding. Regardless of the specific technique, they all join metal parts together by melting the edge of the parts. As a result, forming a metallurgical bond between the pieces links them together firmly.
Assembly
Assembly of sheet metal materials is generally considered the last step of parts-forming processes, which entails the creation of complex metal components.
The final assembly can utilize fastening, welding, and adhesive bonding to create these connections, using bolts and screws or the melting process of welding to meld pieces together. Remember that while the assembly is typically considered the final step in the sheet metal fabrication process, additional steps may be involved depending on the process. Additional steps include applying a powder coating or other coating to cut sheet metal materials.
An expert in sheet metal cutting and fabrication can help a manufacturing company navigate these various steps and determine the right tools, methods, and processes to apply to sheet metal materials to create the optimal final parts.
Steelway Laser Cutting Can Help with the Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
Industries that want to use sheet metal fabrication in their operations will likely need an experienced partner to pave the way. Even different end-goal products require different processes to craft metal parts precisely.
At Steelway Laser Cutting, we specialize in using CNC laser cutting for sheet metal. This helps eliminate any manmade errors or hurdles and results in the highest level of precision.
Laser cutting is effectively a hands-off process. Once the design specifications has been set, the high-power laser beam can work 24/7 to complete the project, regardless of size. The software and the machine completely determine the cutting, bending, punching, or other requirements. As a result, this means less waste, costs, and time involved due to miscalculations or incorrect cuts.
Laser cutting is one of the most effective method for sheet metal fabrication. However, most manufacturing companies don’t have the internal resources to conduct these operations on their own. For the best and most reliable production possible, high quality laser cutting machines and capabilities are a must, as are experienced engineers who can adeptly use these machines for every project.
Sheet Metal Fabrication and Laser Cutting with Steelway Laser Cutting
At Steelway Laser Cutting, we have been providing manufacturing solutions since 1963.Therefore, over the decades, we have adapted the latest machines, methods, and most experienced personnel to laser cut, bend, and weld to our clients’ specific requirements.
We understand how missed deadlines or delays affect your work, and how you need projects completed within a budget. That’s why accuracy is a key component in every job that we handle.
Let’s start a conversation about your sheet metal manufacturing needs, and how our team at Steelway Laser Cutting can help. With an experienced and dedicated resource at your side, you can streamline your sheet metal fabrication processes, without impacting your bottom line.
Article reviewed and approved by Director of Product Design – Derek McAvoy.